FanCheng Съедобные материалы, могут ли есть полностью разлагаемые роботы?
Опубликован в:2020-06-29
Now, for safety reasons, many products that may be swallowed use edible materials, such as edible wax, edible packaging, etc. making a robot with edible materials is about the same size and shape as a capsule. Can such a robot eat? If you can eat it, what do you expect from it? Q cool teeth, oil but not greasy, melt at the entrance? Wait, it doesnt seem to match the human setting of the robot. It should be: it automatically stretches in case of heat and can be controlled by a magnet. After entering the body, it will not only dance like dancing sugar, but also take out the battery swallowed by mistake!
At the 2016 International Conference on Robotics and automation, such an edible capsule robot was unveiled. Four years later, a team of researchers from Johannes keplelinz University in Austria also invented an "edible" robot.
The robot is made of generic biogels based on food grade gelatin. This familiar looking robot is also a little humble - it can be eaten not only by people, but also by microorganisms in sewage within hours.
In the paper entitled Resilient yet entirely degradable gelatin-based biogels for soft robots and electronics (used for manufacturing flexible, completely degradable gelatin based biogels) for electronic products such as mollusks, the research team introduced in detail the robot and the magical materials behind it.

New materials based on gelatin, in this paper, the researchers are straight to the point: Materials drive technological progress. At present, it is mainly used for a series of flexible, self-healing and biocompatible materials, such as robot, which have excellent mechanical properties and self degradability.
However, the research team believes that this material is not durable in the environment and cannot embody all characteristics in one product or platform at the same time. So the team developed a multifunctional gelatin based biogel. This material has strong elasticity, self adhesion, rapid healing, easy replication and scaling, and can be completely degraded during treatment.
It is understood that this material is completely composed of natural ingredients and food grade safety materials, including:
Gelatin: can be completely degraded by human body;
Citric acid: can prevent bacterial growth;
Glycerol: it can prevent bacteria from breeding and dehydration.
What is worth mentioning here is the selection process of basic components by researchers.
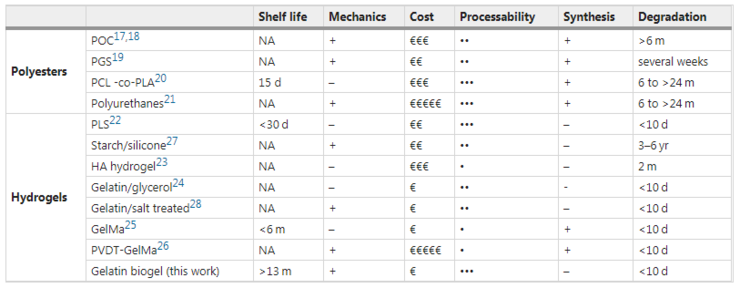
According to the paper, the researchers compared a variety of polyester fibers and hydrogel components to determine a component. The main considerations include the use life, mechanical properties, cost, workability, synthesis and degradation ability.
After comparison, the researchers selected gelatin after Zui (the row below Zui in the table above). Gelatin is available because gelatin based biogels are readily available, without synthesis, and can be added with water-soluble additives. At the same time, due to the fast degradation rate, it is not only harmless to the environment, but also edible.
In fact, many people are not unfamiliar with gelatin. Gelatin is everywhere, from film, food, cosmetics to drugs. At the same time, gelatin has also been used in drug delivery and bone tissue engineering, such as 3D printing organs and manufacturing robots.
In order to test the degradation ability, the research team will immerse the bio gel sheet into deionized water at 23 degree C, and it will dissolve in a few hours. Because of this, the research team said that this bio gel is suitable for temporary installation and frequently updated scenarios. Once triggered, it will be decomposed within a few days and can benefit from transient devices.
In addition, the team also measured the total aerobic decomposition capacity of biological gel through biological oxygen demand (BOD) of microorganisms in wastewater. The results showed that 60% organic compounds could be removed in 10 days. Therefore, based on the biogel developed by the team, researchers may be able to open up new ways of biodegradable applications in water and in vivo.
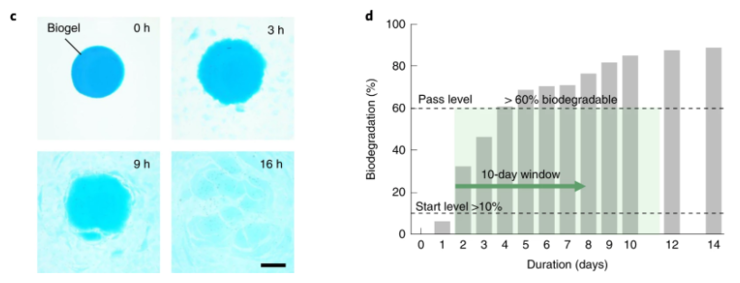
The research team wrote in the paper that this bio gel is a step toward building durable, sustainable software robots and electronic systems. So, what is the robot based on the above materials?
In appearance, the researchers were inspired by elephants. Of course, not only does it look like an elephant, but because of the integration of feedback and control sensors, the robots elephant trunk can also grasp objects.
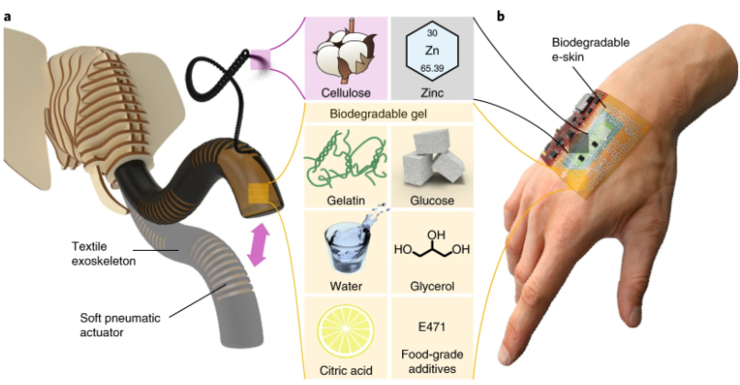
On the basis of the material, the researchers combined the natural materials such as cellulose and zinc on the basis of bio gel. Cellulose is a common structural polysaccharide, which is used as a flexible aero gel actuator framework in dynamic environment. The combination of bio gel and structured zinc electrode can completely degrade the electronic skin (new wearable flexible bionic tactile sensor).
Therefore, from robot components to extendable electronic devices, the whole system is biodegradable. The research team also said: This paves the way for future biomedical devices that simulate our own skin.
As mentioned above, biogels can be completely degraded in the treatment of wastewater, so some people may question the mechanical properties of this robot.
In view of this, the team also explained that bio gel can maintain its mechanical properties under ambient conditions for more than one year. Without failure, the soft brake can withstand more than 330000 cycles.
In addition, the research team said, this robot can be used to deliver drugs in animals in the future.
Martin kaltenbrunner, one of the co authors of the paper, once asked: can we simultaneously develop a material that is very reliable in use and completely degraded when triggered? Now it seems that the team has given the answer with its results.
Last but not least, answer an important question: can robots eat?
According to the research team, although the gels are edible, the original electronic sensors and sensors of the robot are not yet available.
In fact, as early as 2017, the Intelligent Systems Laboratory of the Federal Institute of technology in Lausanne launched an edible robot with a shape similar to soft candy, which can be completely edible and is also made of gelatin.
This kind of robot can be mixed with nutrients, drugs and other components and digested and metabolized by the human body. We can equate the robot with a kind of food.
It can be seen that this robot called medical black technology can be eaten by us. In terms of security, Evan Ackerman, editor of IEEE spectrum, also reassured us:
As far as we know, up to now, there is no edible robot after being eaten, I climbed out of peoples stomachs.
At the 2016 International Conference on Robotics and automation, such an edible capsule robot was unveiled. Four years later, a team of researchers from Johannes keplelinz University in Austria also invented an "edible" robot.

The robot is made of generic biogels based on food grade gelatin. This familiar looking robot is also a little humble - it can be eaten not only by people, but also by microorganisms in sewage within hours.
In the paper entitled Resilient yet entirely degradable gelatin-based biogels for soft robots and electronics (used for manufacturing flexible, completely degradable gelatin based biogels) for electronic products such as mollusks, the research team introduced in detail the robot and the magical materials behind it.

New materials based on gelatin, in this paper, the researchers are straight to the point: Materials drive technological progress. At present, it is mainly used for a series of flexible, self-healing and biocompatible materials, such as robot, which have excellent mechanical properties and self degradability.
However, the research team believes that this material is not durable in the environment and cannot embody all characteristics in one product or platform at the same time. So the team developed a multifunctional gelatin based biogel. This material has strong elasticity, self adhesion, rapid healing, easy replication and scaling, and can be completely degraded during treatment.
It is understood that this material is completely composed of natural ingredients and food grade safety materials, including:
Gelatin: can be completely degraded by human body;
Citric acid: can prevent bacterial growth;
Glycerol: it can prevent bacteria from breeding and dehydration.
What is worth mentioning here is the selection process of basic components by researchers.

According to the paper, the researchers compared a variety of polyester fibers and hydrogel components to determine a component. The main considerations include the use life, mechanical properties, cost, workability, synthesis and degradation ability.
After comparison, the researchers selected gelatin after Zui (the row below Zui in the table above). Gelatin is available because gelatin based biogels are readily available, without synthesis, and can be added with water-soluble additives. At the same time, due to the fast degradation rate, it is not only harmless to the environment, but also edible.
In fact, many people are not unfamiliar with gelatin. Gelatin is everywhere, from film, food, cosmetics to drugs. At the same time, gelatin has also been used in drug delivery and bone tissue engineering, such as 3D printing organs and manufacturing robots.
In order to test the degradation ability, the research team will immerse the bio gel sheet into deionized water at 23 degree C, and it will dissolve in a few hours. Because of this, the research team said that this bio gel is suitable for temporary installation and frequently updated scenarios. Once triggered, it will be decomposed within a few days and can benefit from transient devices.
In addition, the team also measured the total aerobic decomposition capacity of biological gel through biological oxygen demand (BOD) of microorganisms in wastewater. The results showed that 60% organic compounds could be removed in 10 days. Therefore, based on the biogel developed by the team, researchers may be able to open up new ways of biodegradable applications in water and in vivo.

The research team wrote in the paper that this bio gel is a step toward building durable, sustainable software robots and electronic systems. So, what is the robot based on the above materials?
In appearance, the researchers were inspired by elephants. Of course, not only does it look like an elephant, but because of the integration of feedback and control sensors, the robots elephant trunk can also grasp objects.

On the basis of the material, the researchers combined the natural materials such as cellulose and zinc on the basis of bio gel. Cellulose is a common structural polysaccharide, which is used as a flexible aero gel actuator framework in dynamic environment. The combination of bio gel and structured zinc electrode can completely degrade the electronic skin (new wearable flexible bionic tactile sensor).
Therefore, from robot components to extendable electronic devices, the whole system is biodegradable. The research team also said: This paves the way for future biomedical devices that simulate our own skin.
As mentioned above, biogels can be completely degraded in the treatment of wastewater, so some people may question the mechanical properties of this robot.
In view of this, the team also explained that bio gel can maintain its mechanical properties under ambient conditions for more than one year. Without failure, the soft brake can withstand more than 330000 cycles.
In addition, the research team said, this robot can be used to deliver drugs in animals in the future.
Martin kaltenbrunner, one of the co authors of the paper, once asked: can we simultaneously develop a material that is very reliable in use and completely degraded when triggered? Now it seems that the team has given the answer with its results.
Last but not least, answer an important question: can robots eat?
According to the research team, although the gels are edible, the original electronic sensors and sensors of the robot are not yet available.
In fact, as early as 2017, the Intelligent Systems Laboratory of the Federal Institute of technology in Lausanne launched an edible robot with a shape similar to soft candy, which can be completely edible and is also made of gelatin.

This kind of robot can be mixed with nutrients, drugs and other components and digested and metabolized by the human body. We can equate the robot with a kind of food.
It can be seen that this robot called medical black technology can be eaten by us. In terms of security, Evan Ackerman, editor of IEEE spectrum, also reassured us:
As far as we know, up to now, there is no edible robot after being eaten, I climbed out of peoples stomachs.

