Fan Cheng The vigorous development of high-density industrial robot application industry gives b
Опубликован в:2020-07-06
Chinas industrial robots started late and are still in the process of development driven by natural driving forces such as the change of population structure and the increase of labor cost. With the rapid development of industry, China is also facing changes in population structure. In recent years, the proportion of the elderly population has continued to rise, and the labor cost of manufacturing industry has gradually increased.
(1) With the rapid development of industry, China is also facing the problems of aging and high labor cost
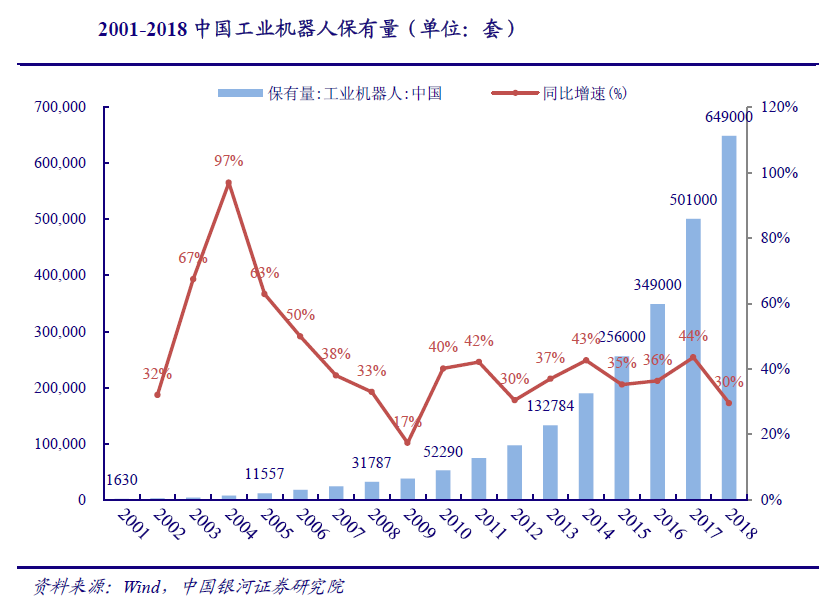
The number of industrial robots in China increased rapidly from 2001 to 2018, from 1630 in 2001 to 649000 in 2018. Meanwhile, from 2001 to 2010, Chinas industrial robots were in the initial stage, with a small base of ownership but rapid growth, with CAGR as high as 47.01%; From 2010 to 2018, the year-on-year growth rate fluctuated around 35%, and the CAGR reached 37.00%.
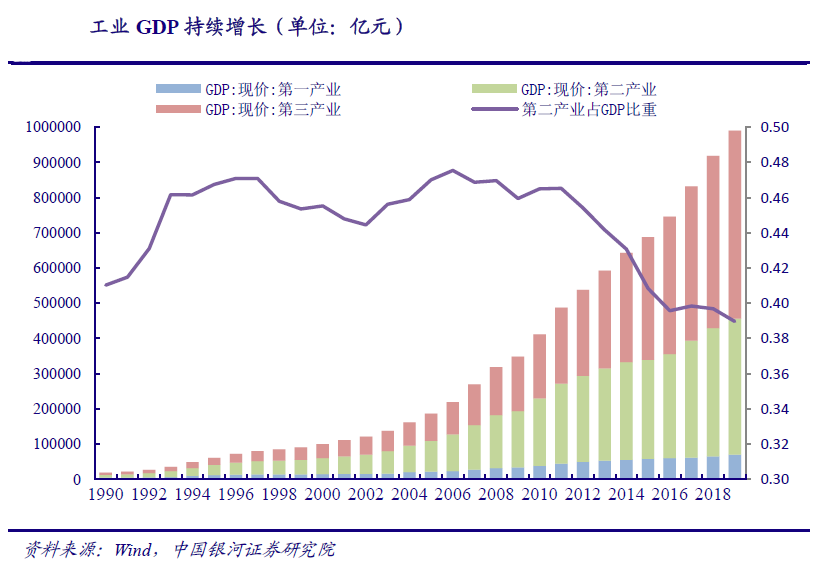
Since the 1990s, Chinas opening-up has increased from coastal cities to the mainland. At the same time, a socialist economic system has been gradually established. Chinas economy has taken off and the demand for industrial production is strong. After entering the 21st century, benefiting from Chinas full accession to the WTO and the rapid development of foreign trade, Chinas economy has ushered in rapid growth. From 2000 to 2010, Chinas total GDP increased from 10028.02 billion yuan to 41211.9 billion yuan, with a CAGR of 15.18%. In this decade, the proportion of industry in GDP has been maintained at about 46% - 48%, making a prominent contribution to economic growth. In 2000, the industrial GDP was 4566.37 billion yuan, which increased to 19162.65 billion yuan in 2010. Although the proportion in GDP decreased, the absolute value continued to increase steadily, and the demand for industrial production continued to be strong.
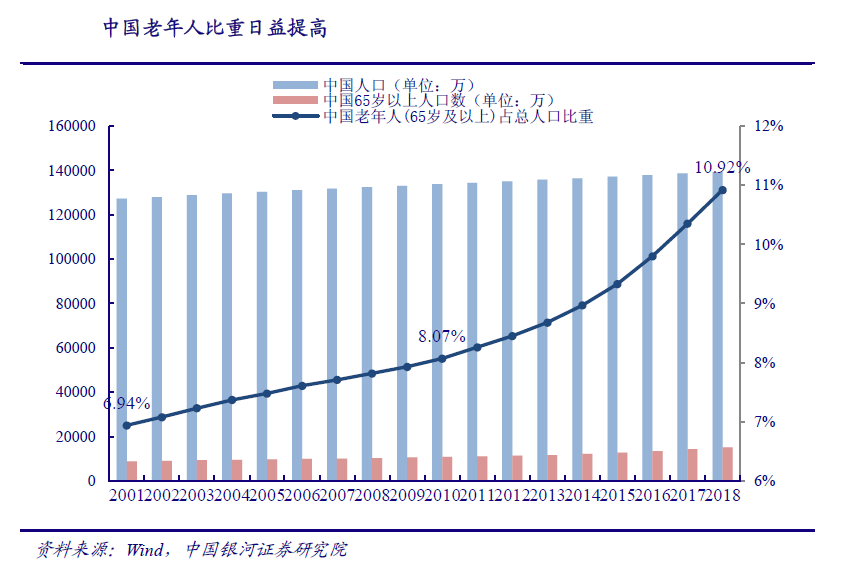
Similarly, with the rapid development of industry, China is also facing changes in the population structure. In recent years, the proportion of the elderly population has continued to rise. From 2000 to 2010, population aging has become the main development trend of Chinas population. In 2001, Chinas total population was 1.272 billion, 88 million people over the age of 65, accounting for 6.94%. In 2010, Chinas total population was 1.338 billion, 108 million people over the age of 65, accounting for 8.07%, According to the international standard that more than 7% of the population aged 65 and over can be called the elderly population, China has entered an elderly society, and the problem of aging has gradually become prominent.
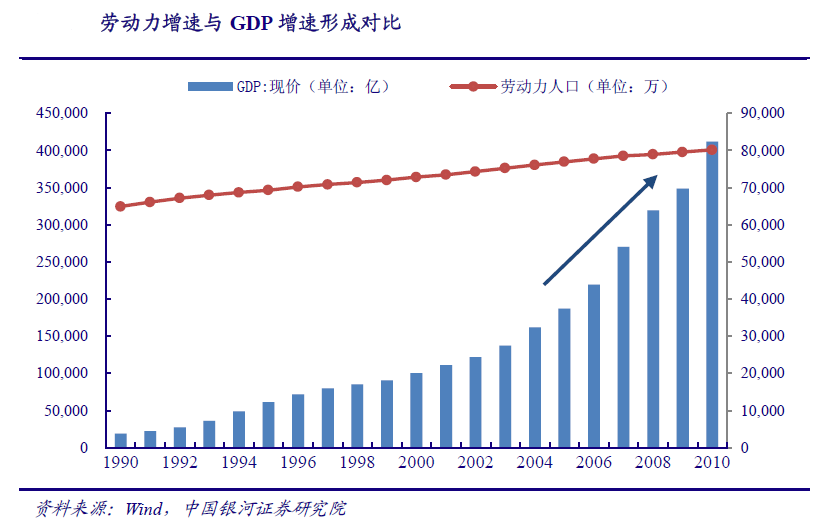
The slow growth of labor force is in contrast to the rapid economic growth. After 1983, China began to implement the family planning policy, and the newly born population decreased. Therefore, the growth rate of the labor force population began to slow down after entering the 21st century. The labor force population was 649 million in 1990, 728 million in 2000, 1.16% in 1990-2000, 802 million in 2010 and 0.97% in 2000-2010. However, from 2000 to 2010, Chinas economy was in a state of rapid growth. The total GDP increased from 10028.02 billion yuan to 41219.9 billion yuan, and the CAGR was as high as 15.18%. The slow growth of the labor force population was significantly compared with the high growth rate of GDP.
The change of population structure leads to the shortage of labor, and Chinas industrial robots usher in the first development. After the rudimentary period from 1972 to 1985 and the long period of technology research and development from 1985 to 2000, Chinas industrial robots finally embarked on the road of industrialization and began the rapid development of the rudimentary period due to the shortage of labor force. In 2001, the number of industrial robots in China was only 1630, which soared to 52290 in 2010, with a CAGR of 47.01%.
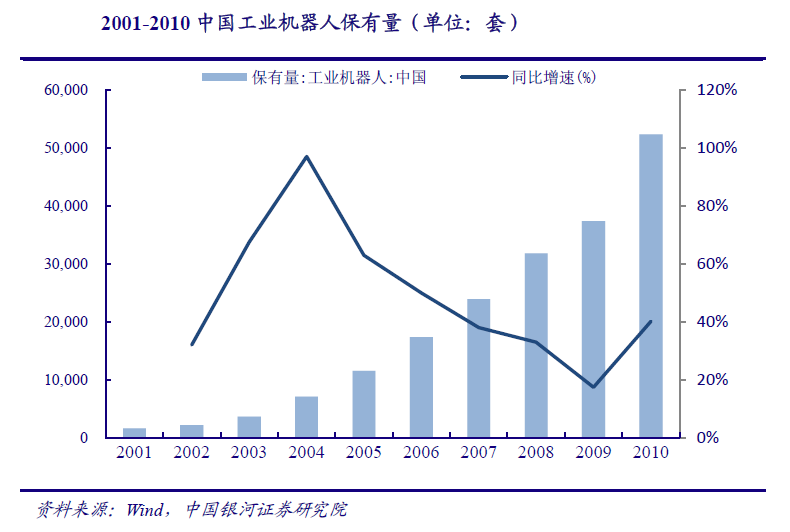
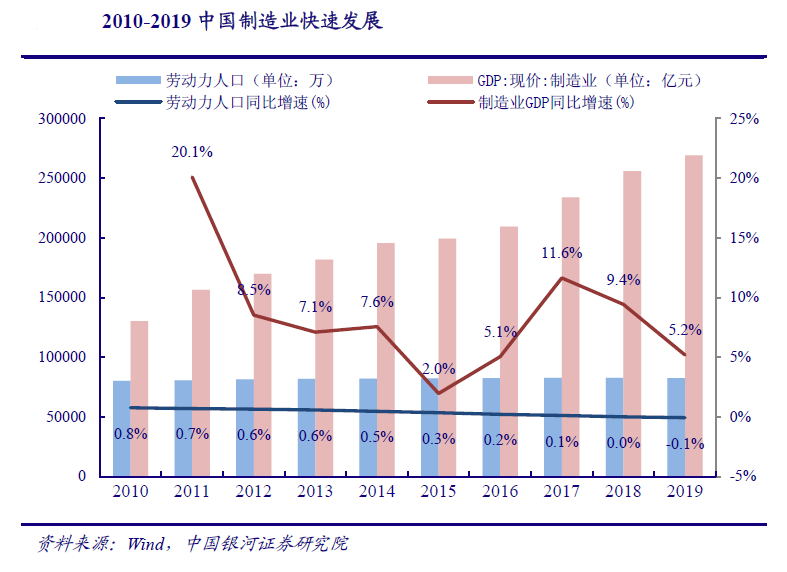
The manufacturing industry has developed rapidly, and the labor force continues to be in short supply. The Fifth Plenary Session of the 17th CPC Central Committee in 2010 defined the theme and strategic task of national development during the 12th Five Year Plan period. It is necessary to accelerate the development of modern industrial system and transform and improve the manufacturing industry. Therefore, Chinas manufacturing industry has gradually changed from labor-intensive to technology intensive, improving the core competitiveness of the industry. From 2010 to 2019, Chinas manufacturing industry ushered in rapid growth. In 2010, the manufacturing GDP was 13 trillion yuan, which increased to 27 trillion yuan in 2019, cagr8 40%。 The rapid development of manufacturing industry puts forward higher demand for labor force, but during this period, Chinas aging problem is becoming more and more serious. The proportion of the elderly in the total population increased from 8.07% in 2010 to 10.92%, and the CAGR of the labor force population decreased from 0.97% in 2000-2010 to 0.33%. The labor force is in short supply.
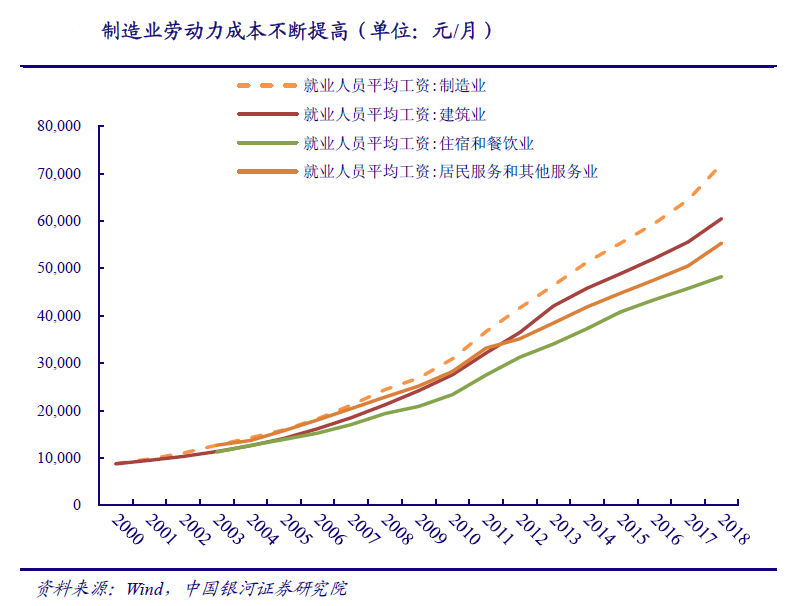
There is a continuous shortage of labor, and the labor cost of manufacturing industry is gradually increasing. From 2010 to 2018, the shortage of labor force promoted the increase of wages in various industries, but the growth rate of manufacturing industry was significantly higher than that of other industries. In 2010, the average wages of employees in Chinas manufacturing industry, residential service and other service industries, construction industry, accommodation and catering industry were 30916, 28206, 27529 and 23382 yuan / year respectively. The average wages in manufacturing industry were 9.60%, 12.3% and 32.22% higher than those in residential service and other service industries, construction industry, accommodation and catering industry respectively. In 2018, the average wages of employees in Chinas manufacturing industry, construction industry, residential service and other service industries, accommodation and catering industry were 72088, 60501, 55343 and 48 respectively, 260 yuan / year. The average wage of manufacturing industry is 19.15%, 30.26% and 49.37% higher than that of construction industry, residential service and other service industries, accommodation and catering industry respectively.
The sharp increase in labor costs has driven the increase in the density of industrial robots in China. The development of industrial robots is closely related to the manufacturing industry. Due to the increasing labor cost in the manufacturing industry, more and more enterprises take industrial robots as a substitute for labor, and industrial robots have ushered in the explosive growth in the second stage. In 2011, the density of industrial robots in China was 10 sets / 10000 workers, and in 2018, it has increased to 140 sets / 10000 workers, cagr33 35%。

(2) The development potential of Chinas automobile and 3C industries is still large, and the incremental demand space of industrial robots can be expected
Although the deployment density of industrial robots in China in 2018 (140 sets / 10000 workers) has exceeded the world average (99 sets / 10000 workers), there is still a large gap with the deployment density of advanced manufacturing countries such as Japan, South Korea and Germany. From the sales of domestic industrial robots, most robots are used in automobile manufacturing, computer and communication electronic equipment manufacturing, which is more consistent with the situation of other countries.
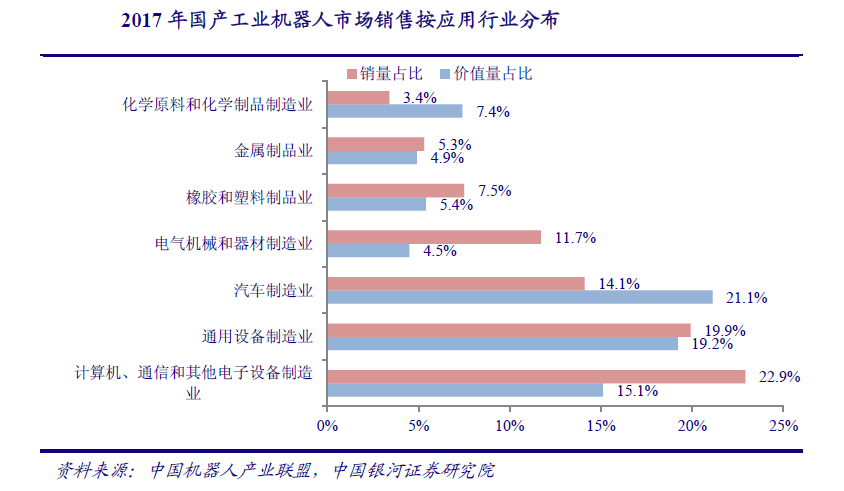
Chinas downstream application industry of industrial robots has not yet entered the stage of transformation and upgrading, and industries with more application of industrial robots such as automobile and 3C have not yet entered the ranks of the first echelon in the world. Therefore, the driving force for the growth of industrial robots is still from the natural driving force of population to the driving force of industrial upgrading, and there is still room for significant growth in the ownership and density in the future.
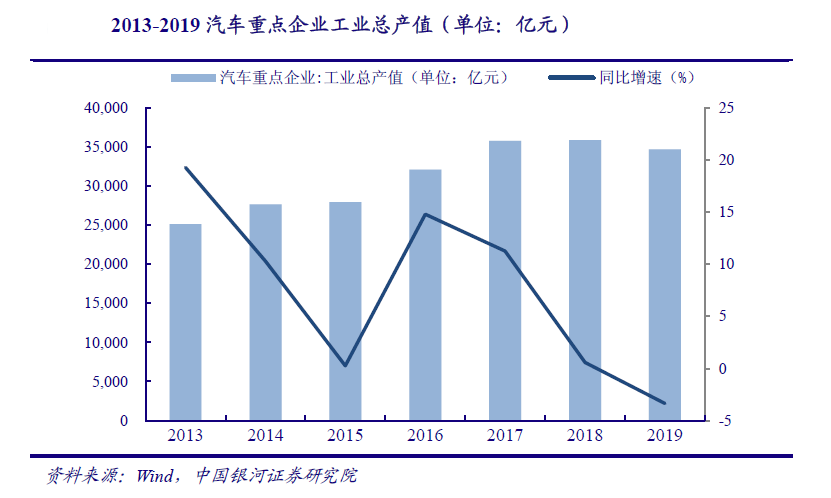
With consumption stimulation and industrial upgrading, the total output value of the automobile industry is still expected to grow continuously. In the past decade, with the rapid growth of Chinas economy, the consumption capacity of residents has been steadily improved, and the automobile industry has developed rapidly. In 2013, the total industrial output value of key automobile enterprises was 2.5 trillion, which increased to 3.5 trillion in 2019, cagr5.5 trillion 8%, and car sales also rose steadily, from 18.06 million in 2010 to 2.7 million in 2018, 8.08 million. Although the growth rate of the automobile industry has slowed down in the past year or two, in the long run, the improvement of automobile configuration, the increase of the proportion of localized parts, the rapid development of new technologies such as electrification, intelligence and interconnection, as well as the expansion and opening-up of the domestic automobile industry will contribute to the upgrading of the automobile industry. Chinas automobile market still has great room for development, Therefore, the number of industrial robots is expected to increase.
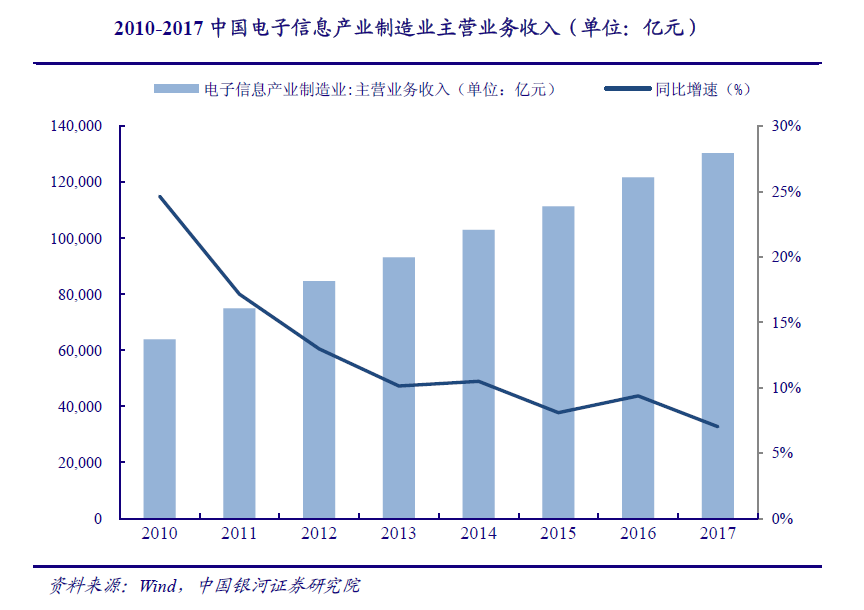
The 3C industry, which is fast, repetitive and high-precision, still has a large demand for industrial robots. In recent years, the improvement of Chinas scientific and technological level has driven the development of new technologies, new processes and new equipment of 3C manufacturing enterprises, forming product competitiveness, and Chinas 3C industry has achieved rapid development. The main business income of Chinas electronic information industry manufacturing industry was 6.4 trillion yuan in 2010 and about 13 trillion yuan in 2017, nearly doubling. At present, the traditional 3C industry represented by smart phones, tablets and traditional PCs has gradually entered the Red Sea market of stock competition. The future development of traditional 3C products will be oriented by innovation, optimization and localization, especially in the field of hardware. The technology competition and competition will become more intense, and the demand for hardware production equipment will gradually increase, because we believe that Repeated and high-precision 3C industry still has a large demand for industrial robots.
Benefiting from the improvement of automation technology, aquatic products and the change of population structure, Chinas industrial robots ushered in preliminary development, and the number of industrial robots increased from 1630 to 52290. Since 2010, due to the continuous increase of labor cost caused by the change of population structure, Chinas industrial robots continue to maintain the momentum of rapid growth. In 2011, the density of industrial robots in China was 10 sets / 10000 workers, and in 2018, it has increased to 140 sets / 10000 workers, with CAGR as high as 33.35%. Current car & amp; 3C is the main application field of industrial robot, Chinas automobile & amp; The contribution rate of output value of 3C industry to GDP in 2018 was 14.07%. We believe that part of the future incremental space of Chinas industrial robots will benefit from the upgrading space of automobile and 3C industry.
*** In addition, with the implementation of made in China 2025, Chinas strategy of building a manufacturing power is also gradually advancing. In the future, it has become a general trend to focus on the development of high-end manufacturing industry and grasp the lifeline of core key technologies. As the main fields of high-end manufacturing industry, there is no doubt about the localization of core products. China in automotive & amp; There is a huge demand market in 3C field, and industrial upgrading will be carried out gradually. The independent brands of Chinas automobile industry are moving towards well-known and first-class, and the 3C electronic industry is expected to follow the leading pace of 5g development, which are expected to become the driving force for the development of Chinas industrial robots to the third stage, and the ownership and deployment density are expected to develop by leaps and bounds.
In conclusion, the main driving forces for the explosive growth of industrial robots in a country in the early stage are generally the change of population structure and the surge of labor costs, which are confirmed by the relevant data of Japan, Germany and South Korea. After that, with the basic solution of the prominent contradiction of labor force, the industrial characteristics of various countries (such as whether they have developed downstream application industries) have become the differentiation point of the demand for industrial robots in different countries. Compared with many other advanced countries or regions such as Japan and Germany, the ownership of industrial robots tends to be flat; 3C industry is the pillar industry of South Korea. Therefore, driven by industrial demand, South Korean industrial robots showed a rapid growth trend during this period. At the same time, in contrast to China, Chinas industrial robots started late and are still in the process of development driven by natural driving forces such as the change of population structure and the increase of labor cost. The upgrading and development potential of Chinas automobile and 3C industries is huge, and the incremental demand space for industrial robots can be expected. In the long run, Chinas industrial robots are also expected to usher in greater development space driven by the upgrading of downstream industries in the future.
(1) With the rapid development of industry, China is also facing the problems of aging and high labor cost
The number of industrial robots in China increased rapidly from 2001 to 2018, from 1630 in 2001 to 649000 in 2018. Meanwhile, from 2001 to 2010, Chinas industrial robots were in the initial stage, with a small base of ownership but rapid growth, with CAGR as high as 47.01%; From 2010 to 2018, the year-on-year growth rate fluctuated around 35%, and the CAGR reached 37.00%.

Since the 1990s, Chinas opening-up has increased from coastal cities to the mainland. At the same time, a socialist economic system has been gradually established. Chinas economy has taken off and the demand for industrial production is strong. After entering the 21st century, benefiting from Chinas full accession to the WTO and the rapid development of foreign trade, Chinas economy has ushered in rapid growth. From 2000 to 2010, Chinas total GDP increased from 10028.02 billion yuan to 41211.9 billion yuan, with a CAGR of 15.18%. In this decade, the proportion of industry in GDP has been maintained at about 46% - 48%, making a prominent contribution to economic growth. In 2000, the industrial GDP was 4566.37 billion yuan, which increased to 19162.65 billion yuan in 2010. Although the proportion in GDP decreased, the absolute value continued to increase steadily, and the demand for industrial production continued to be strong.

Similarly, with the rapid development of industry, China is also facing changes in the population structure. In recent years, the proportion of the elderly population has continued to rise. From 2000 to 2010, population aging has become the main development trend of Chinas population. In 2001, Chinas total population was 1.272 billion, 88 million people over the age of 65, accounting for 6.94%. In 2010, Chinas total population was 1.338 billion, 108 million people over the age of 65, accounting for 8.07%, According to the international standard that more than 7% of the population aged 65 and over can be called the elderly population, China has entered an elderly society, and the problem of aging has gradually become prominent.

The slow growth of labor force is in contrast to the rapid economic growth. After 1983, China began to implement the family planning policy, and the newly born population decreased. Therefore, the growth rate of the labor force population began to slow down after entering the 21st century. The labor force population was 649 million in 1990, 728 million in 2000, 1.16% in 1990-2000, 802 million in 2010 and 0.97% in 2000-2010. However, from 2000 to 2010, Chinas economy was in a state of rapid growth. The total GDP increased from 10028.02 billion yuan to 41219.9 billion yuan, and the CAGR was as high as 15.18%. The slow growth of the labor force population was significantly compared with the high growth rate of GDP.

The change of population structure leads to the shortage of labor, and Chinas industrial robots usher in the first development. After the rudimentary period from 1972 to 1985 and the long period of technology research and development from 1985 to 2000, Chinas industrial robots finally embarked on the road of industrialization and began the rapid development of the rudimentary period due to the shortage of labor force. In 2001, the number of industrial robots in China was only 1630, which soared to 52290 in 2010, with a CAGR of 47.01%.

The manufacturing industry has developed rapidly, and the labor force continues to be in short supply. The Fifth Plenary Session of the 17th CPC Central Committee in 2010 defined the theme and strategic task of national development during the 12th Five Year Plan period. It is necessary to accelerate the development of modern industrial system and transform and improve the manufacturing industry. Therefore, Chinas manufacturing industry has gradually changed from labor-intensive to technology intensive, improving the core competitiveness of the industry. From 2010 to 2019, Chinas manufacturing industry ushered in rapid growth. In 2010, the manufacturing GDP was 13 trillion yuan, which increased to 27 trillion yuan in 2019, cagr8 40%。 The rapid development of manufacturing industry puts forward higher demand for labor force, but during this period, Chinas aging problem is becoming more and more serious. The proportion of the elderly in the total population increased from 8.07% in 2010 to 10.92%, and the CAGR of the labor force population decreased from 0.97% in 2000-2010 to 0.33%. The labor force is in short supply.

There is a continuous shortage of labor, and the labor cost of manufacturing industry is gradually increasing. From 2010 to 2018, the shortage of labor force promoted the increase of wages in various industries, but the growth rate of manufacturing industry was significantly higher than that of other industries. In 2010, the average wages of employees in Chinas manufacturing industry, residential service and other service industries, construction industry, accommodation and catering industry were 30916, 28206, 27529 and 23382 yuan / year respectively. The average wages in manufacturing industry were 9.60%, 12.3% and 32.22% higher than those in residential service and other service industries, construction industry, accommodation and catering industry respectively. In 2018, the average wages of employees in Chinas manufacturing industry, construction industry, residential service and other service industries, accommodation and catering industry were 72088, 60501, 55343 and 48 respectively, 260 yuan / year. The average wage of manufacturing industry is 19.15%, 30.26% and 49.37% higher than that of construction industry, residential service and other service industries, accommodation and catering industry respectively.

The sharp increase in labor costs has driven the increase in the density of industrial robots in China. The development of industrial robots is closely related to the manufacturing industry. Due to the increasing labor cost in the manufacturing industry, more and more enterprises take industrial robots as a substitute for labor, and industrial robots have ushered in the explosive growth in the second stage. In 2011, the density of industrial robots in China was 10 sets / 10000 workers, and in 2018, it has increased to 140 sets / 10000 workers, cagr33 35%。

(2) The development potential of Chinas automobile and 3C industries is still large, and the incremental demand space of industrial robots can be expected
Although the deployment density of industrial robots in China in 2018 (140 sets / 10000 workers) has exceeded the world average (99 sets / 10000 workers), there is still a large gap with the deployment density of advanced manufacturing countries such as Japan, South Korea and Germany. From the sales of domestic industrial robots, most robots are used in automobile manufacturing, computer and communication electronic equipment manufacturing, which is more consistent with the situation of other countries.

Chinas downstream application industry of industrial robots has not yet entered the stage of transformation and upgrading, and industries with more application of industrial robots such as automobile and 3C have not yet entered the ranks of the first echelon in the world. Therefore, the driving force for the growth of industrial robots is still from the natural driving force of population to the driving force of industrial upgrading, and there is still room for significant growth in the ownership and density in the future.
With consumption stimulation and industrial upgrading, the total output value of the automobile industry is still expected to grow continuously. In the past decade, with the rapid growth of Chinas economy, the consumption capacity of residents has been steadily improved, and the automobile industry has developed rapidly. In 2013, the total industrial output value of key automobile enterprises was 2.5 trillion, which increased to 3.5 trillion in 2019, cagr5.5 trillion 8%, and car sales also rose steadily, from 18.06 million in 2010 to 2.7 million in 2018, 8.08 million. Although the growth rate of the automobile industry has slowed down in the past year or two, in the long run, the improvement of automobile configuration, the increase of the proportion of localized parts, the rapid development of new technologies such as electrification, intelligence and interconnection, as well as the expansion and opening-up of the domestic automobile industry will contribute to the upgrading of the automobile industry. Chinas automobile market still has great room for development, Therefore, the number of industrial robots is expected to increase.

The 3C industry, which is fast, repetitive and high-precision, still has a large demand for industrial robots. In recent years, the improvement of Chinas scientific and technological level has driven the development of new technologies, new processes and new equipment of 3C manufacturing enterprises, forming product competitiveness, and Chinas 3C industry has achieved rapid development. The main business income of Chinas electronic information industry manufacturing industry was 6.4 trillion yuan in 2010 and about 13 trillion yuan in 2017, nearly doubling. At present, the traditional 3C industry represented by smart phones, tablets and traditional PCs has gradually entered the Red Sea market of stock competition. The future development of traditional 3C products will be oriented by innovation, optimization and localization, especially in the field of hardware. The technology competition and competition will become more intense, and the demand for hardware production equipment will gradually increase, because we believe that Repeated and high-precision 3C industry still has a large demand for industrial robots.

Benefiting from the improvement of automation technology, aquatic products and the change of population structure, Chinas industrial robots ushered in preliminary development, and the number of industrial robots increased from 1630 to 52290. Since 2010, due to the continuous increase of labor cost caused by the change of population structure, Chinas industrial robots continue to maintain the momentum of rapid growth. In 2011, the density of industrial robots in China was 10 sets / 10000 workers, and in 2018, it has increased to 140 sets / 10000 workers, with CAGR as high as 33.35%. Current car & amp; 3C is the main application field of industrial robot, Chinas automobile & amp; The contribution rate of output value of 3C industry to GDP in 2018 was 14.07%. We believe that part of the future incremental space of Chinas industrial robots will benefit from the upgrading space of automobile and 3C industry.
*** In addition, with the implementation of made in China 2025, Chinas strategy of building a manufacturing power is also gradually advancing. In the future, it has become a general trend to focus on the development of high-end manufacturing industry and grasp the lifeline of core key technologies. As the main fields of high-end manufacturing industry, there is no doubt about the localization of core products. China in automotive & amp; There is a huge demand market in 3C field, and industrial upgrading will be carried out gradually. The independent brands of Chinas automobile industry are moving towards well-known and first-class, and the 3C electronic industry is expected to follow the leading pace of 5g development, which are expected to become the driving force for the development of Chinas industrial robots to the third stage, and the ownership and deployment density are expected to develop by leaps and bounds.
In conclusion, the main driving forces for the explosive growth of industrial robots in a country in the early stage are generally the change of population structure and the surge of labor costs, which are confirmed by the relevant data of Japan, Germany and South Korea. After that, with the basic solution of the prominent contradiction of labor force, the industrial characteristics of various countries (such as whether they have developed downstream application industries) have become the differentiation point of the demand for industrial robots in different countries. Compared with many other advanced countries or regions such as Japan and Germany, the ownership of industrial robots tends to be flat; 3C industry is the pillar industry of South Korea. Therefore, driven by industrial demand, South Korean industrial robots showed a rapid growth trend during this period. At the same time, in contrast to China, Chinas industrial robots started late and are still in the process of development driven by natural driving forces such as the change of population structure and the increase of labor cost. The upgrading and development potential of Chinas automobile and 3C industries is huge, and the incremental demand space for industrial robots can be expected. In the long run, Chinas industrial robots are also expected to usher in greater development space driven by the upgrading of downstream industries in the future.

